Speed of Sound Wave In A Fluid-
Before you go through this article, make sure that you have gone through the previous article on Speed of Sound Wave in Fluids.
We have learnt that-
- The speed of sound wave through a fluid is determined by the bulk modulus and density of the fluid.
- The speed of sound wave through a fluid is given by the formula-
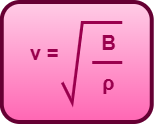
- A given solid or a liquid has a fixed value of bulk modulus but so is not the case for gases.
- The value of bulk modulus of a gas depends on the process.
In this article, we will learn about Newton’s Formula for speed of sound in a gas.
Newton’s Formula For Speed of Sound In A Gas-
As a sound wave travels through air, the segments of the medium are subjected to a series of compressions and rarefactions.
Newton suggested that-
- The temperature variations in an element due to compressions and rarefactions are negligible.
- When a small element of air gets compressed, the amount of heat produced during compression is lost to the surroundings and thus the temperature remains constant.
- Similarly, when a rarefaction arrives, the amount of heat lost during rarefaction is gained from the surroundings and thus the temperature again remains constant.
- Such a process in which volume and pressure of a gas changes but temperature remains constant is called an isothermal process.
In such a process, the gas satisfies the equation-
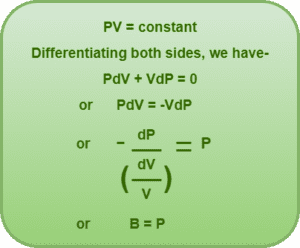
It means the bulk modulus of an ideal gas in an isothermal process is equal to the pressure of the gas.
Substituting in the formula v = √(B/ρ), we get-

This formula is called as Newton’s formula for the speed of sound in a gas.
Calculating Speed of Sound Using Newton’s Formula-
Let us now use Newton’s formula to calculate the speed of sound in air at NTP.
At NTP, we have-
- P = 1 atm = 1.013 x 105 Pa
- ρ = 1.293 kg/m3
Substituting in the formula, we have-

Experimentally, the speed of sound in air at NTP is 332 m/s.
Thus, the value of speed of sound calculated using Newton’s formula is less than the experimental value of the speed of sound.
Error in Newton’s Formula-
Difference between the experimental value of speed of sound in air and the value calculated using Newton’s formula
= 332 – 280
= 52 m/s
Thus, percentage error in the calculated value is given by-
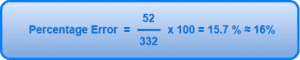
Such a large error could not be taken as an experimental error. Newton put forward a number of arguments to explain the above discrepancy but none of them was satisfactory.
Later, a French mathematician & physicist, Laplace explained the exact cause of discrepancy.
Test Your Concepts-
Newton’s Formula For Speed of Sound Wave in Gas
Next Article-
Get more notes & other study material of the Chapter Waves.
