Work-
In physics, work may be defined as-
| The work is said to be done when a force acting on the body causes a displacement it in the direction of force. |
Essential Conditions for Work-
The following conditions must be satisfied for work to be done-
- A force must act on the body.
- The point of application of the force must have some displacement in the direction of force.
Work Done By A Constant Force-
The work done by a constant force is calculated by using the formula-

OR

Consider-
- A body is acted upon by a force ‘F’ acting at an angle θ with the horizontal.
- The body suffers a displacement ‘d’ as shown.
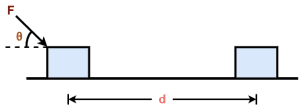
Here, the force F can be resolved into two rectangular components-
- Fsinθ, which is perpendicular to the direction of displacement
- Fcosθ, which is along the direction of displacement
The component Fcosθ causes the displacement d in its own direction whereas the component Fsinθ does not cause any displacement.
By the above definition, the work done by force F is given by-
W = Force in the direction of displacement x Displacement
W = Fcosθ x d
W = F x d x cosθ
W = F.d
Thus, work done is the dot product of force and displacement vectors.
Characteristics of Work done-
- Work is a scalar quantity.
- The SI unit of work is joule (J).
1 J = 1 Nm
- The work done is said to be one joule if a force of 1 N causes a displacement of 1 m in the direction of force.
- The work done by a force may be positive, negative or zero.
Nature of Work Done-
The work done by a force may be positive, negative or zero.
Positive Work-
| When the angle between force and displacement is an acute angle (<90°), then the work done by force is positive. |
The positive work signifies that the force favors the motion of the body.
Examples-
- When a body falls freely under gravity (θ=0°), the work done by gravity is positive.
- When a horse pulls a cart, the applied force and displacement are in the same direction (θ=0°), the work done by horse is positive.
Negative Work-
| When the angle between force and displacement is an obtuse angle (>90°), then the work done by force is negative. |
The negative work signifies that the direction of force is such that it opposes the motion of the body.
Examples-
- When a body is thrown upwards under gravity (θ=180°), the work done by gravity is negative.
- When brakes are applied to a moving vehicle (θ=180°), the work done by the braking force is negative.
- The work done by friction is usually negative.
Zero Work-
| When the angle between force and displacement is 90°, then the work done by force is zero. |
Examples-
- The work done by a coolie carrying a suitcase on his head and moving on a horizontal platform (θ=90°) is zero.
- The work done by centripetal force (θ=90°) is zero.
Read the next article on-
Work Done By A Variable Force
Get more notes & other study material of the Chapter Work, Energy & Power.

