Parameters of Motion-
The motion of a body may be described through the following parameters-
- Distance
- Displacement
- Speed
- Velocity
- Acceleration
- Jerk
In this article, we will discuss about distance and displacement.
Distance-
| It is the total length of the actual path traveled by a body between its initial and final positions. |
Characteristics of Distance-
- The SI unit of distance is meter (m).
- It has only magnitude and no direction. Hence, it is a scalar quantity.
- It can never be negative. It is always positive or zero.
Displacement-
| It is the shortest distance measured in the direction from initial position to the final position. |
Characteristics of Displacement-
- The SI unit of displacement is meter (m).
- It has both magnitude and direction. Hence, it is a vector quantity.
- It may be positive, negative or zero.
Example of Distance & Displacement-
Consider four cities A, B, C and D located as shown-
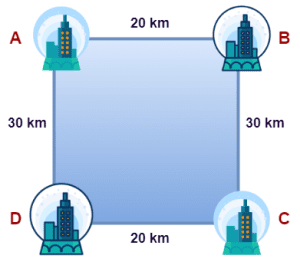
A salesman starts from city A, goes to city B, then to city C and then to city D. Then,
Distance traveled by the salesman
= Length of the actual path covered
= AB + BC + CD
= 20 km + 30 km + 20 km
= 70 km
Magnitude of displacement of the salesman
= Shortest distance between the initial and final position
= Shortest distance between city A and city D
= 30 km
Important Notes-
Note-01:
- The distance traveled by a body is always greater than or equal to the magnitude of displacement.
- The distance and displacement are same when body moves along a straight line path without taking any turn.
In general,

Note-02:
The displacement of the body is always zero if it returns back to its initial position.
Note-03:
The displacement of a body is independent of the choice of the origin of the position coordinates.
Differences Between Distance & Displacement-
The following table shows the differences between distance and displacement-
Distance |
Displacement |
| It is the total length of the actual path traveled by a body between its initial and final positions. | It is the shortest distance measured in the direction from initial position to the final position. |
| It is a scalar quantity. | It is a vector quantity. |
| The distance covered by a body depends on the path followed by the body. | The displacement covered by a body does not depend on the path followed by the body. |
| Distance can never decrease with time. | Displacement may decrease with time. |
| It can never be negative. It is always positive or zero. | It may be positive, negative or zero. |
| There is always a distance covered whenever there is a motion. | There may be no displacement even when the body has moved.
It is possible when body comes back to its initial position. |
| It is always greater than or equal to the magnitude of displacement. | It is always less than or equal to the distance covered. |
Read the next article on-
Get more notes and other study material of Motion in One Dimension.

