Stress & Strain | Mechanical Properties of Solids-
Before you go through this article, make sure that you have gone through the previous articles on Stress and Strain.
We have learnt-
- When a deforming force is applied on a body, a restoring force is produced in it.
- This restoring force per unit area of the body is called as stress.
- The effect of stress is to produce distortion or change the configuration of the body.
- The ratio of the change in configuration to the original configuration is called as strain.
- Strain measures the degree of deformation.
In this article, we will learn about Hooke’s Law and Modulus of Elasticity.
Hooke’s Law-
In mechanical properties of solids, Hooke’s law is defined as-
| For sufficiently small stresses, stress is directly proportional to the strain. |
Mathematically,
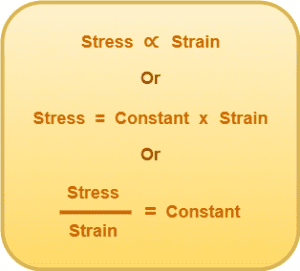
Here, this constant is called Modulus of Elasticity or Elastic Modulus. Thus,

Characteristics of Modulus of Elasticity-
- Its SI unit is same as that of stress i.e. newton per square meter (Nm-2) or pascal (Pa).
- Its dimensional formula is same as that of stress i.e. [ML-1T-2].
- It is a scalar quantity.
- Its value depends on the nature of material of the body and is independent of its dimensions.
- It is a measure of rigidity or stiffness of a material. Greater the modulus, the stiffer the material.
Types of Modulus of Elasticity-
Since strain is of three types, therefore modulus of elasticity is also of three types-
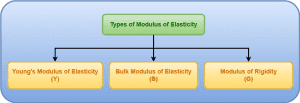
Let us discuss all types of modulus of elasticity one by one in detail.
1. Young’s Modulus of Elasticity-
It is defined as the ratio of the longitudinal stress on the material to the longitudinal strain produced in the material.

2. Bulk Modulus of Elasticity-
It is defined as the ratio of the bulk stress (or volume stress) on the material to the volume strain produced in the material.

3. Shear Modulus or Modulus of Rigidity-
It is defined as the ratio of the tangential stress (or shearing stress) on the material to the shear strain produced in the material.

Read the next article on-
Elastic Potential Energy In Stretched Wire
Get more notes & other study material of the Chapter Mechanical Properties of Solids.

