Magnetism-
| Magnetism is a phenomenon associated with the magnetic fields which arise from the motion of electric charges. |
This motion can take many forms.
- It can be an electric current in a conductor.
- It can be charged particles moving through space.
- It can be the motion of an electron in an atomic model.
Types of Magnetism-
Magnetism can be divided into two classes-
- Pure Magnetism
- Electromagnetism
Pure Magnetism-
Pure magnetism deals with iron magnets also called as permanent magnets.
A magnet is a material that creates an invisible field called as magnetic field around itself in which its magnetic effects like-
- attracting other ferromagnetic materials such as iron, nickel, cobalt etc
- and attracting or repelling other magnets can be experienced.
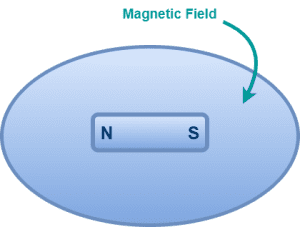
Until 1820, only this kind of magnetism was known.
Electromagnetism-
|
In 1820, a Danish physicist, Hans Christian Oersted while demonstrating the flow of electric current in a wire to his friends noticed that the current causes a nearby compass needle to move.
This image is showing- Oersted (right) and his assistant holding a wire over a compass needle in a north-south direction. The compass needle is then deflected.
Based on the fact that a magnetic needle can be deflected only by a magnetic field, he concluded that- A current carrying wire produces a magnetic field around it. |
- Electromagnetism is a branch of physics that deals with the study of electricity, magnetism & how they are connected.
- Electromagnetism deals with electromagnets.
- An electromagnet is a temporary magnet that only generates a magnetic field when electric current is flowing through it.
- This makes electromagnets very convenient and controllable since they can easily be turned on or off.
Characteristics of Magnetic Field-
- Magnetic field is a vector quantity which has both magnitude and direction.
- The SI unit of magnetic field is tesla (T) named after the great scientist Nikola Tesla.
- The CGS unit of magnetic field is gauss (G).
- Other units of magnetic field are NA-1m-1 and Wb m-2. (These units would be derived later)

Next Article-
Get more notes & other study material of the Chapter Moving Charges & Magnetism.


