Electric Dipole-
| A system of two equal and opposite charges separated by a small distance is called as an electric dipole. |
For example- two charges +q and -q separated by a small distance 2ℓ constitute an electric dipole.
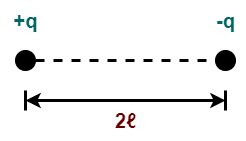
Here,
- The distance (2ℓ) between the two charges is called as dipole length.
- The mid point of the line joining +q and -q charges is called as center of the electric dipole.
Charge On An Electric Dipole-
By additive nature of electric charge, we have-
| Total charge on an electric dipole = +q + (-q) = 0 |
However, the charge on an electric dipole is equal to the magnitude of either charge of the electric dipole.
For example- If charge on an electric dipole is 5 µC, then one charge is +5 µC and the other charge is -5 µC.
Also Read- Properties of Electric Charge
Examples of Electric Dipoles-
The examples of electric dipoles are-
- Molecules of water (H2O)
- Molecules of ammonia (NH3)
- Molecules of hydrochloric acid (HCl)
- Molecules of carbon dioxide (CO2)
- Molecules of sodium chloride (NaCl)
- Molecules of alcohol etc
Electric Dipole Moment-
| Electric dipole moment of an electric dipole is defined as the product of the magnitude of either charge of the electric dipole and the dipole length. |
It is a vector quantity having its direction from negative to positive charge. It is denoted by p.

Mathematically,

- The magnitude of electric dipole moment is p = q x 2ℓ.
- The direction of electric dipole moment is from negative to positive charge.
- The SI unit of electric dipole moment is coulomb meter (C m).
- The dimensional formula of electric dipole moment is [M0L1T1A1].
Read the next article on-
Electric Field Due To Electric Dipole
Get more notes & other study material of the Chapter Electric Charges & Field.

