Electric Dipole-
Before you go through this article, make sure that you have gone through the previous article on Electric Dipole.
We have learnt-
- A system of two equal and opposite charges separated by a small distance is called as electric dipole.
- Electric dipole moment of an electric dipole is defined as the product of magnitude of either charge and the dipole length having its direction from -q to +q.
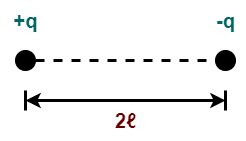
Electric Dipole
In this article, we will discuss Electric dipole In Uniform Electric Field.
Electric Dipole In Uniform Electric Field-
Consider-
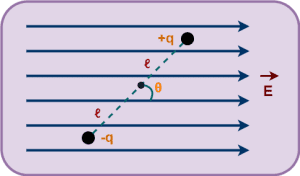
- An electric dipole consisting of two charges -q and +q separated by a distance of 2ℓ.
- The electric dipole is placed in a uniform electric field.
- The electric dipole moment vector of the electric dipole makes an angle θ with the electric field.
This is shown below-
Force On Electric Dipole In Uniform Electric Field-
We know,
- A positive charge always experiences a force in the direction of electric field.
- A negative charge always experiences a force in the direction opposite to electric field.
So, Force exerted on charge +q is given by-

So, Force exerted on charge -q is given by-
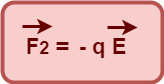
These two forces on the electric dipole may be represented as-

Now, by superposition principle, the net force on the electric dipole in the uniform electric field is given by-
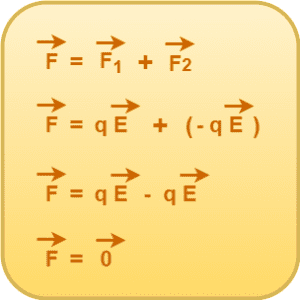
|
Thus,
There is no net force acting on the electric dipole in uniform electric field. So, it does not perform a translational motion. |
Torque On Electric Dipole In Uniform Electric Field-
- The two equal and opposite forces acting on the electric dipole forms a couple.
- This couple tends to rotate the dipole in the electric field by exerting a torque on it.
The torque acting due to the couple is given by-

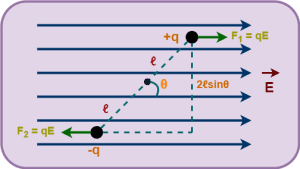
We put-
- Magnitude of Force = qE
- Perpendicular distance between the two forces = 2ℓsinθ
Substituting the values, the torque on the electric dipole is calculated as-
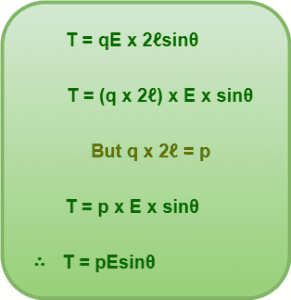
Thus, torque on an electric dipole in a uniform electric field is given by-

In vector form,

|
Thus,
An electric dipole experiences a torque in a uniform electric field given by T = pEsinθ. So, it performs a rotatory motion. |
Special Cases-
Case-01: When electric dipole is parallel to the electric field (θ=0°)-

In this case, the torque experienced by the electric dipole is given by-
T = pEsin0° = 0
Thus, when electric dipole gets aligned with the electric field, the torque becomes zero.
In this position, the electric dipole is in stable equilibrium.
Case-02: When electric dipole is anti-parallel to the electric field (θ=180°)-
In this case, the torque experienced by the electric dipole is given by-
T = pEsin180° = 0
Thus, when electric dipole gets aligned in the direction opposite to the electric field, the torque becomes zero.
In this position, the electric dipole is in unstable equilibrium.
Case-03: When electric dipole is perpendicular to the electric field (θ=90°)-

In this case, the torque experienced by the electric dipole is given by-
T = pEsin90° = pE (maximum)
Thus, when electric dipole is perpendicular to the electric field, it experiences the maximum torque.
In this position, the electric dipole experiences the maximum torque.
Electric Dipole In Non-Uniform Electric Field-
In non-uniform electric field,
- The +q and -q charges of the electric dipole experience different forces (not equal and opposite). Hence, a net force acts on the electric dipole in non-uniform electric field.
- Also, a net torque acts on the electric dipole which depends on the location of the dipole in the field.
| Thus, an electric dipole experiences a force as well as a torque in a non-uniform electric field. |
Read the next article on-
Get more notes & other study material of the Chapter Electric Charges & Field.

