Gauss’s Law-
Before you go through this article, make sure that you have gone through the previous article on Gauss’s Law.
We have learnt-
- Gauss’s Law helps to find the total electric flux through any closed surface.
- It states that the total electric flux through any closed surface is 1/εo times the net charge enclosed within it.
Applications of Gauss’s Law-
Using Gauss’s law, we can easily calculate the electric field due to a-
- thin infinite long line charge
- thin infinite plane sheet of charge
- uniformly charged thin spherical shell
In this article, we will discuss the electric field due to a thin infinite plane sheet of charge.
Electric Field Due To A Thin Infinite Plane Sheet Of Charge-
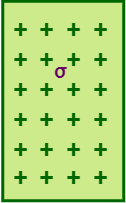
Consider a thin infinite plane sheet having a uniform surface charge density σ Cm-2 as shown-
Direction of Electric Field-
By symmetry, the electric field due to a plane sheet of charge is directed-
- perpendicularly outwards if the sheet carries a positive charge
- perpendicularly inwards if the sheet carries a negative charge
Magnitude of Electric Field-
To calculate the magnitude of electric field intensity E at a point P located at a distance r from the sheet using Gauss’s law, we consider an imaginary closed cylinder of length r on each side of the sheet with end caps of area A as the Gaussian surface.
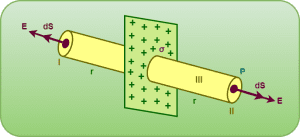
A cylinderical Gaussian surface is an ideal choice because-
At every point on the curved surface of cylinder,
- the angle between electric field intensity and area element is 90°.
- So, the electric flux passing through it will be zero.
At every point on the end caps of cylinder,
- the magnitude of electric field intensity is constant.
- the angle between electric field intensity and area element is 0°.
According to Gauss’s theorem, we have-

(Equation-01)
The cylinderical Gaussian surface can be divided into three parts-
- Left end cap
- Right end cap
- Curved surface
Then, equation-01 can be written as-

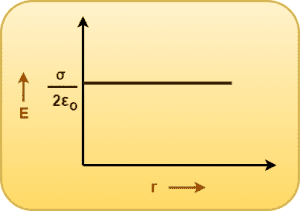
Graph-
Clearly, the electric field intensity due to a thin infinite plane sheet of charge is independent of the distance of observation point from the sheet i.e.

The graph showing the variation of electric field intensity due to a thin infinite plane sheet of charge with distance from it is-
Also Check-
- Electric field due to a thin Infinite long line charge
- Electric field due to a charged thin spherical shell
Read the next article on-
Electric Field Due To Charged Thin Spherical Shell
Get more notes & other study material of the Chapter Electric Charges & Field.

