Wheatstone Bridge-
Before you go through this article, make sure that you have gone through the previous article on Wheatstone Bridge.
We have learnt-
- A Wheatstone bridge is an arrangement of four resistances used to determine one of these resistances in terms of the remaining three resistances.
- It is a null method and is preferred over the other methods for determining the value of an unknown resistance.
In this article, we will learn about Meter Bridge.
Meter Bridge-
| Meter bridge is the practical application of the Wheatstone bridge that is used to measure an unknown resistance. |
Principle-
Its working is based on the principle of Wheatstone bridge. When the bridge is balanced, we have-
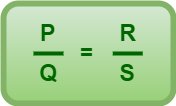
Construction-
- It consists of a one meter long manganin wire of uniform cross-section.
- The wire is stretched along a meter scale fixed over a wooden board.
- The two ends of the wire are soldered to two L-shaped thick copper strips A and C.
- Between these two copper strips, another copper strip is fixed so as to provide two gaps.
- A resistance box is connected in one gap and the unknown resistance in the other gap.
- A source of emf E is connected across AC.
- A movable jockey and a galvanometer are connected across BD as shown in the figure.
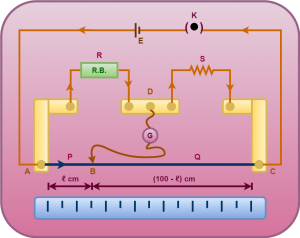
METER BRIDGE
Working-
- A suitable resistance R is taken out from the resistance box.
- Then, the jockey is moved along the wire AC till there is no deflection in the galvanometer.
- This is the balanced condition of the Wheatstone bridge.
If P and Q are the resistances of the parts AB and BC of the wire, then for the balanced condition of the Wheatstone bridge, we have-
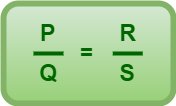
Let AB = ℓ cm, then BC = (100 – ℓ) cm.
Since the wire is of uniform cross-section, therefore-
Resistance of wire ∝ Length of wire
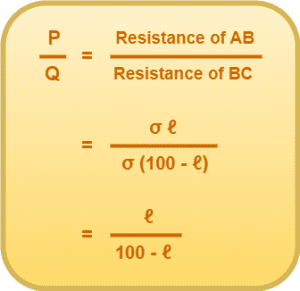
where σ is the resistance per unit length of the wire.
Hence,
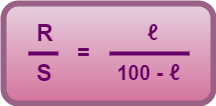
From here,

Knowing the values of ℓ and R, the value of unknown resistance S can be determined.
Determination of Resistivity-
If r is the radius of the wire and L is its length, then resistivity of its material is given by-

Test Your Concepts-
Next Article-
Get more notes & other study material of the Chapter Current Electricity.

