Mechanism of Current Flow In A Conductor-
Before you go through this article, make sure that you have gone through the previous article on Mechanism of Current Flow In A Conductor.
We have learnt-
- When a potential difference is applied across the ends of a conductor, an electric field is created inside it.
- The electric field applies an electric force on the free electrons inside the conductor.
- As a result, they start drifting in a preferred direction and the flow of current starts.
In this article, we will learn about resistance & conductance of a conductor.
Resistance of Conductor-
The resistance of a conductor is defined as-
| The property of a conductor by virtue of which it opposes the flow of charge carriers through it is called as its resistance. |
Any material that has a property of offering resistance is called as a resistor.
Cause of Resistance-
- When free electrons drift inside the conductor, they frequently collide with the positive metal ions.
- The collisions of free electrons with the positive metal ions is the main cause of resistance of the conductor.
Calculation of Resistance-
The resistance of a conductor is equal to the ratio of potential difference applied across the conductor to the current flowing through it.
Mathematically,

SI Unit of Resistance-
- The SI unit of resistance is ohm (Ω).
- The resistance of a conductor is said to be one ohm if a current of 1 A flows through it when a potential difference of 1 V is applied across its ends.
Factors Affecting Resistance-
The resistance of a conductor depends upon the following factors-
1. Length of Conductor-
- The resistance of a conductor increases with the increase in its length.
- Thus, resistance of a conductor is directly proportional to its length i.e.
R ∝ L
2. Cross-sectional Area of Conductor-
- The resistance of a conductor decreases with the increase in its cross-sectional area.
- Thus, resistance of a conductor is inversely proportional to its cross-sectional area i.e.
R ∝ 1/A
3. Nature of Material of Conductor-
- The resistance of a conductor also depends on the nature of material of the conductor.
- For example- the resistance of nichrome wire is 60 times that of a copper wire of same length and same area of cross-section.
4. Temperature of Conductor-
- The resistance of a conductor increases with the increase in its temperature.
- With the rise in temperature, the collisions of free electrons with the other free electrons and with the positive metal ions increases.
- Due to increased collisions, the resistance of conductor also increases.
At a constant temperature, on combining the above factors, we get-

OR

Here, ρ is a constant of proportionality called as resistivity or specific resistance of the material of the conductor.
Conductance of Conductor-
| The conductance of a conductor is the ease with which charge carriers can flow through it. |
- More is the resistance of a conductor, lesser is its conductance and vice-versa.
- So, conductance of a conductor is defined as the reciprocal of resistance of the conductor.
- It is denoted by the symbol G.
Mathematically,

OR
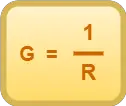
The SI unit of conductance is ohm-1 or mho or siemens (S).
Test Your Concepts-
Quiz on Resistance & Conductance
Next Article-
Temperature Dependence of Resistance
Get more notes & other study material of the Chapter Current Electricity.

